USE CASE: Low-code and edge Intelligence for smart factories
By combining Low-Code and Edge Intelligence, manufacturing sites can establish and upgrade flexible production capabilities. This innovative approach empowers the industry to adapt quickly, achieve individualized production, and stay ahead in the evolving manufacturing landscape. The future of manufacturing is here with SmartEdge’s transformative technologies.
In the future of manufacturing, the focus is shifting towards producing small series of highly individualized products, replacing large-scale specialized factories. To meet the challenges of individualized production, the SmartEdge project introduces smart factories that integrate and enrich shop floor data with standardized information models. Leveraging Low-Code and Edge Intelligence, these factories enable flexible and cost-effective production, revolutionizing the manufacturing industry.
![Revolutionizing Industry: low code and edge intelligence (Illustration by Susanne Gold). Working in the cloud: * share what you want to share * get the support you need.] [Low-code and Edge Intelligence: * keep data confidential * integated AI * work with real-time data * reprogramme easily and quickly](https://www.smart-edge.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/image2-blogpost-UC4.png)
Revolutionizing Industry: low-code and edge intelligence – Openness, Simplicity, Flexibility, Efficiency & Security (Illustration by Susanne Gold).
Empowering Flexibility
Traditional manufacturing systems designed for mass production lack the agility needed in today’s rapidly changing market. Shorter product life cycles and the demand for individualization require adaptable systems that can quickly respond to evolving needs. Local smart factories, based on modular production, are the solution to producing small series of highly individualized products efficiently and economically. These factories need to offer a wide product variety and flexibility while maintaining high efficiency with small batch sizes.
Optimizing Performance and Upgrading Capabilities
SmartEdge’s Low-Code and Edge Intelligence approach automates the integration of new production capabilities into existing automation systems. Industrial applications are created using a low-code visual environment, instantiated from recipes with drag-and-drop functions. Recipes serve as application templates, configured to retrieve data from field devices via standardized communication interfaces. These low-code applications can be deployed at the edge or in the cloud, with a focus on edge deployment for low-latency data processing. Edge Intelligence further enhances the system by bringing artificial intelligence directly into industrial devices, represented as reusable recipes that can be easily configured and deployed.
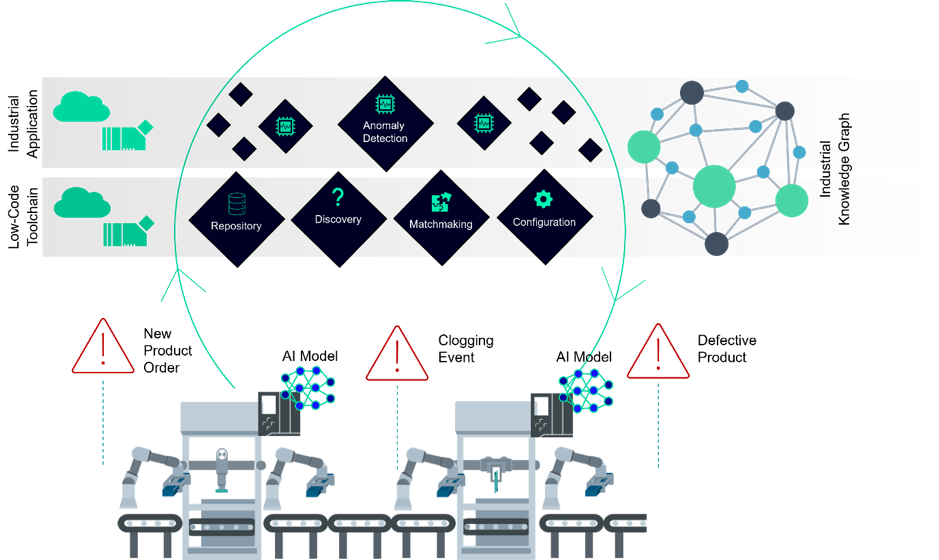
Low-Code Edge Intelligence in SmartEdge
Low-Code Edge Intelligence in SmartEdge
Implementation
The innovative solution will be implemented within a simulated manufacturing environment at Siemens’ cutting-edge facility in Fuerth, Germany. The implementation will involve the integration of advanced technologies, primarily focused on the utilization of Siemens SIMATIC S7-1500 controllers. These controllers will empower the production modules, forming the heart of the demonstrator. To enhance their capabilities, Neural Processing Units, will be seamlessly integrated, enabling them to execute artificial intelligence models directly at the edge. This integration will not only enable efficient control of devices but also facilitate the seamless operation of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs).
Furthermore, the implementation will incorporate a range of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, each running distributed TinyML AI models. This distributed approach ensures optimal utilization of resources while maximizing efficiency. To streamline the development process, SmartEdge will leverage the Mendix low-code platform. This versatile platform will serve as a robust foundation, offering continuous semantic integration of brownfield and heterogeneous IoT devices. Additionally, it will enable the creation and orchestration of recipe-based Edge Intelligence applications.
By combining these advanced technologies and leveraging the capabilities of Siemens’ manufacturing facility, the proposed solution aims to revolutionize manufacturing processes, enhancing productivity, and paving the way for intelligent, autonomous systems.
Authors: Dr. Darko Anicic (Siemens AG), Dr. Aparna Thuluva (Siemens AG), Kirill Dorofeev (Siemens AG) and Haoyu Ren (Siemens AG)
References:
[1] [SWJ20] Aparna Saisree Thuluva, Darko Anicic, Sebastian Rudolph, Malintha Adikari: Semantic Node-RED for rapid development of interoperable industrial IoT applications. Semantic Web Journal, IOS Press 2020.
[2] [OTM17] Aparna Saisree Thuluva, Kirill Dorofeev, Monika Wenger, Darko Anicic, Sebastian Rudolph: Semantic-Based Approach for Low-Effort Engineering of Automation Systems. OTM Conferences 2017.
[3] [IJCNN21] Haoyu Ren, Darko Anicic, Thomas A. Runkler: TinyOL: TinyML with Online-Learning on Microcontrollers. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IJCNN 2021.
